2025年被称为“体重管理年”,从饮食控制到新型减重手段,人们对健康瘦的追求愈发理性。自1990年以来,全球成人肥胖率增长逾一倍,2022年,超重成年人口已达25亿,其中8.9亿人为肥胖。 [1]《体重管理指导原则》指出,若当前超重这一趋势不能得到有效控制,到2030年时,全国范围内成人超重肥胖率预计会达到70.5%,而儿童的这一比例将上升至31.8%。 [2]
在此背景下,应对肥胖的措施层出不穷,例如禁食、断食、药物辅助等等,但一个被多数人忽视的问题正在凸显:减重时,肌肉可能比脂肪跑得更快。Aker BioMarine(阿克海洋生物人类营养公司,以下简称“阿克人类营养”)的最新研究为这个难题带来了新答案,阿克人类营养磷虾油能在减重期间为肌肉撑起保护伞,让健康减重更有力量。
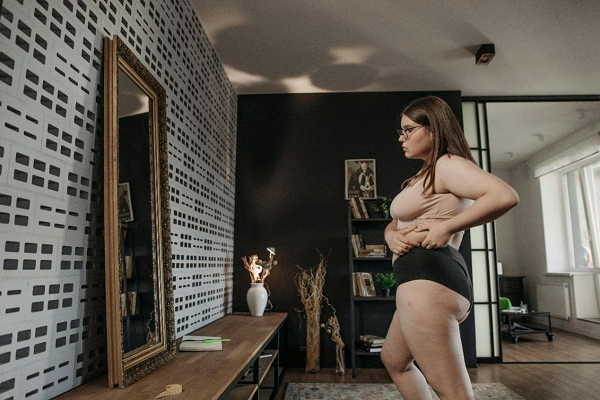

减重,别让肌肉掉队
瘦了5斤,却感觉力气小了一大截?这不是错觉,减重时大部分体重下降来自肌肉等非脂肪组织,而使用隔日禁食、热门减重药物等方式时,可能导致肌肉流失更明显。据研究表明,约25-30%的体重减轻来自去脂体重(FFM),其中包括宝贵的肌肉。这不仅导致力量下降、功能受损,还可能引发长期的代谢健康问题。[3-8]
尤其是GLP-1受体激动剂等减重药物兴起,虽然显著减轻了体重,但数据揭示,减重总量中有高达25%到39%可能是肌肉量的流失。这一速度远超自然衰老过程中的肌肉衰减,若处理不当,将引发潜在的长远健康风险。

磷虾油,给减重加个肌肉防护盾
在减重期间,肌肉流失是个让人头疼的问题,不过磷虾油凭借其独特的胆碱和磷脂型 Omega-3 脂肪酸营养组合,在减重过程中,既能守护肌肉,又能让减重更健康、更高效。
胆碱是生成肌肉收缩必需的乙酰胆碱的前体物质,不仅能助力肌肉正常运作,还能在减重时抑制脂肪酸的生成,促进肌肉生长。[10]
磷脂型 Omega-3 脂肪酸能促进肌肉蛋白质合成,让肌肉更有力量,还能缓解炎症反应,降低肌肉在减重期间受损的风险。简而言之,磷虾油在减重过程中,既能守护肌肉,又能让减重更健康、更高效。[11-15]

据阿克人类营养最新发表在《Obesity》期刊的一项研究显示,在隔日禁食减重期间补充阿克磷虾油,能更有效地维持去脂体重、肌肉力量及身体功能。另外磷虾油组的收缩压和炎症标志物(如TNF-α、CRP)也显著降低,这就是整体代谢健康变好的铁证。
此外,另一项临床研究也证实了磷虾油能显著改善握力、膝关节伸展力和大腿肌肉厚度,对增强肌肉质量和功能的潜力也得到了验证。
不止护肌肉,磷虾油更有多重健康惊喜:
在追求健康体态的道路上,可靠的科学支持尤为重要。阿克人类营养开展的50余项人体临床试验证实磷虾油对心脏、关节、肝脏、皮肤健康等多方面有益。在体重管理领域,这种多效合一的特性使其成为值得关注的营养选择。减重从来不是与数字的博弈,而是一场倾听身体需求的对话。2025年,在国家"体重管理年"行动的推动下,我们对健康的追求已超越单纯的体重秤数字,转向脂肪与肌肉的动态平衡。作为深耕大健康领域的践行者,阿克将南极磷虾的天然馈赠融入体重管理,响应"健康中国2030"的召唤。
当运动成为日常,当营养回归天然,减重与增肌不再矛盾。选择天然营养补剂,以海洋智慧平衡身心,开启一场既减重又增肌的健康之旅。科学守护健康,迎接更美好的自己。

[1] WHO. Obesity and overweight: Factsheet. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO); 2024. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact- sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight. Accessed March 29, 2024. [cited 2024 28 March].
[2] 国家卫生健康委,体重管理指导原则(2024年版),2024
[3] Turicchi, J., R. O’Driscoll, G. Finlayson, C. Duarte, M. Hopkins, N. Martins, J. Michalowska, T.M. Larsen, M.A. van Baak, A. Astrup, and R.J. Stubbs, Associations between the proportion of fat-free mass loss during weight loss, changes in appetite, and subsequent weight change: results from a randomized 2-stage dietary intervention trial. Am J Clin Nutr, 2020. 111(3): p. 536-544.
[4] Chaston, T.B., J. Dixon, and P.E. O’Brien, Changes in fat-free mass during significant weight loss: a systematic review. Int J Obes, 2007. 31(5): p. 743-750.
[5] Frimel, T.N., D.R. Sinacore, and D.T. Villareal, Exercise attenuates the weight- loss-induced reduction in muscle mass in frail obese older adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 2008. 40(7): p. 1213.
[6] Zibellini, J., R. Seimon, C. Lee, A. Gibson, M. Hsu, and A. Sainsbury, Effect of diet‐induced weight loss on muscle strength in adults with overweight or obesity–a systematic review and meta‐analysis of clinical trials. Obes Rev, 2016. 17(8): p. 647-663.
[7] Bosy-Westphal, A., B. Schautz, M. Lagerpusch, M. Pourhassan, W. Braun, K. Goele, M. Heller, C. Glüer, and M. Müller, Effect of weight loss and regain on adipose tissue distribution, composition of lean mass and resting energy expenditure in young overweight and obese adults. Int J Obes, 2013. 37(10): p. 1371-1377.
[8] Lagacé, J.C., M. Brochu, and I.J. Dionne, A counterintuitive perspective for the role of fat‐free mass in metabolic health. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2020. 11(2): p. 343-347.
[9] Conte, C., K.D. Hall, and S. Klein, Is Weight Loss–Induced Muscle Mass Loss Clinically Relevant? JAMA, 2024.
[10] Moretti, A., M. Paoletta, S. Liguori, M. Bertone, G. Toro, and G. Iolascon, Choline: an essential nutrient for skeletal muscle. Nutrients, 2020. 12(7): p. 2144.
[11] Xu, D., Y. Lu, X. Yang, D. Pan, Y. Wang, S. Yin, S. Wang, and G. Sun, Effects of fish oil-derived n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid on body composition, muscle strength and physical performance in older people: a secondary analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Age Ageing, 2022. 51(12):p. afac274.
[12] Alkhedhairi, S.A., F.F.A. Alkhayl, A.D. Ismail, A. Rozendaal, M. German, B. MacLean, L. Johnston, A.A. Miller, A.M. Hunter, and L.J. Macgregor, The effect of krill oil supplementation on skeletal muscle function and size in older adults: A randomised controlled trial. Clin Nutr, 2022. 41: p. 1228-1235.
[13] Dupont, J., L. Dedeyne, S. Dalle, K. Koppo, and E. Gielen, The role of omega-3 in the prevention and treatment of sarcopenia. Aging Clin Exp Res, 2019. 31(6): p. 825-836.
[14] Di Girolamo, F.G., R. Situlin, S. Mazzucco, R. Valentini, G. Toigo, and G. Biolo, Omega-3 fatty acids and protein metabolism: enhancement of anabolic interventions for sarcopenia. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care, 2014. 17(2): p. 145-150.
[15] Gao, K., L. Chen, M. Yang, L. Han, S. Yiguang, H. Zhao, X. Chen, W. Hu, H. Liang, and J. Luo, Marine n-3 PUFA protects hearts from I/R injury via restoration of mitochondrial function. Scandinavian Cardiovascular Journal, 2015. 49(5): p. 264-269.
Gray, S.R. and B. Mittendorfer, Fish oil-derived n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids for the prevention and treatment of sarcopenia. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care, 2018. 21(2): p. 104-109.




